KI für DeFi-Datenanalyse: Ein praktischer On-Chain-Workflow
KI für DeFi-Datenanalyse: Ein praktischer On-Chain-Workflow dreht sich darum, transparente, aber chaotische Blockchain-Aktivitäten in wiederholbare Forschung zu verwandeln: saubere Datensätze, verteidigbare Merkmale, testbare Hypothesen und überwachte Modelle. Wenn Sie jemals TVL-Dashboards, Ertragsseiten und Token-Diagramme angesehen und gedacht haben „das fühlt sich vage an“, ist dieser Workflow Ihr Gegenmittel. Und wenn Sie strukturierte, gestufte Analysen mögen (so wie SimianX AI mehrstufige Forschungszyklen gestaltet), können Sie die gleiche Disziplin in die On-Chain-Arbeit einbringen, sodass die Ergebnisse erklärbar, protokollübergreifend vergleichbar und einfach iterierbar sind.
Warum die Analyse von On-Chain-Daten schwieriger (und besser) ist, als es aussieht
On-Chain-Daten geben Ihnen die Grundwahrheit darüber, was passiert ist: Übertragungen, Tauschgeschäfte, Kredite, Liquidationen, Staking, Governance-Abstimmungen und Gebührenflüsse. Aber „Grundwahrheit“ bedeutet nicht „einfache Wahrheit“. DeFi-Analysten stoßen auf Probleme wie:
Der Vorteil ist riesig: Wenn Sie eine KI-bereite Pipeline aufbauen, können Sie Fragen mit Beweisen beantworten, nicht mit Gefühlen – und dann denselben Workflow immer wieder ausführen, während sich die Bedingungen ändern.
Schritt 0: Beginnen Sie mit einer Entscheidung, nicht mit einem Datensatz
Der schnellste Weg, Zeit in DeFi zu verschwenden, besteht darin, „alles herunterzuladen“ und zu hoffen, dass Muster auftauchen. Definieren Sie stattdessen:
1. Entscheidung: Was werden Sie basierend auf der Analyse anders machen?
2. Objekt: Protokoll, Pool, Token, Vault-Strategie oder Wallet-Kohorte?
3. Zeithorizont: Intraday, wöchentlich, vierteljährlich?
4. Ergebnismetrik: Was zählt als Erfolg oder Misserfolg?
Beispielentscheidungen, die gut zu KI passen
Wichtige Erkenntnis: KI ist am stärksten, wenn das Ziel messbar ist (z. B. Rückgangswahrscheinlichkeit, Liquidationshäufigkeit, Verhältnis von Gebühren zu Emissionen), nicht wenn das Ziel „gute Erzählung“ ist.
Schritt 1: Bauen Sie Ihre On-Chain-Datenbasis auf (Quellen + Reproduzierbarkeit)
Ein praktischer On-Chain-Workflow benötigt zwei Ebenen: rohe Kettenwahrheit und angereicherten Kontext.
A. Rohe Kettenwahrheit (kanonische Eingaben)
Planen Sie mindestens Folgendes zu sammeln:
Profi-Tipp: Behandle jeden Datensatz als versionierten Snapshot:
B. Anreicherung (Kontext, den du für "Bedeutung" benötigst)
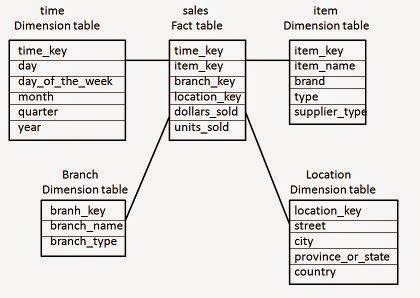
Minimales reproduzierbares Schema (was du in deinem Lager haben möchtest)
Denke in „Faktentabellen“ und „Dimensionen“:
fact_swaps(chain, block_time, tx_hash, pool, token_in, token_out, amount_in, amount_out, trader, fee_paid)fact_borrows(chain, block_time, market, borrower, asset, amount, rate_mode, health_factor)dim_address(address, label, type, confidence, source)dim_token(token, decimals, is_wrapped, underlying, risk_flags)dim_pool(pool, protocol, pool_type, fee_tier, token0, token1)Verwende inline code-Benennungen konsistent, damit nachgelagerte Funktionen nicht brechen.
Schritt 2: Normalisiere Entitäten (Adressen → Akteure)
KI-Modelle denken nicht in Hex-Zeichenfolgen; sie lernen aus Verhaltensmustern. Deine Aufgabe ist es, Adressen, wo möglich, in stabile „Entitäten“ umzuwandeln.
Praktischer Ansatz zur Kennzeichnung (schnell → besser)
Beginne mit drei Ebenen:
Was für jedes Label gespeichert werden soll
label (z. B. „MEV-Bot“, „Protokollkasse“)confidence (0–1)evidence (ausgelöste Regeln, Heuristiken, Links)valid_from / valid_to (Bezeichnungen ändern sich!)Wallet-Clustering: Halte es konservativ
Clustering kann helfen (z. B. Adressen, die von einem Betreiber kontrolliert werden, gruppieren), aber es kann auch dein Dataset vergiften, wenn es falsch ist.
| Entitätsaufgabe | Was es freischaltet | Häufige Fallstricke |
|---|---|---|
| Vertragsklassifizierung | Protokoll-Ebene Merkmale | Proxy-/Upgrade-Muster führen in die Irre |
| Wallet-Clustering | Kohortenflüsse | Falsche Zusammenführungen von gemeinsamen Geldgebern |
| Bot-Erkennung | Saubere „organische“ Signale | Label-Drift, während Bots sich anpassen |
| Treasury-Identifizierung | Analyse der realen Rendite | Vermischung von Treasury- vs. Benutzergebühren |
Schritt 3: Feature-Engineering für DeFi (die „wirtschaftliche Wahrheit“ Ebene)
Hier wird KI nützlich. Dein Modell lernt aus Merkmalen – also entwerfe Merkmale, die Mechanismen widerspiegeln, nicht nur „Zahlen“.
A. DEX- & Liquiditätsmerkmale (Ausführungsrealität)
Nützliche Merkmale sind:
Fette Regel: Wenn dir Handelsfähigkeit wichtig ist, modelliere Slippage unter Stress, nicht „durchschnittliches Tagesvolumen“.
B. Kreditmerkmale (Insolvenz & Reflexivität)
C. “Realer Ertrag” vs Anreiz-Ertrag (Kern der Nachhaltigkeit)
DeFi-Erträge mischen oft:
Eine praktische Zerlegung:
brutto_ertrag = gebühren_ertrag + anreiz_ertragrealer_ertrag ≈ gebühren_ertrag - verwässerungskosten (wobei die Verwässerungskosten kontextabhängig sind, aber Sie sollten zumindest die Emissionen als Prozentsatz der Marktkapitalisierung und des Wachstums des zirkulierenden Angebots verfolgen)Wichtige Erkenntnis: nachhaltiger Ertrag ist selten der höchste Ertrag. Es ist der Ertrag, der überlebt, wenn die Anreize nachlassen.
Schritt 4: Ziel beschriften (was Sie möchten, dass das Modell vorhersagt)
Viele DeFi-Datensätze scheitern, weil die Labels vage sind. Gute Ziele sind spezifisch und messbar.
Beispiele für Modellziele
Vermeiden Sie Label-Leckagen
Wenn Ihr Label zukünftige Informationen verwendet (wie eine spätere Ausnutzung), stellen Sie sicher, dass Ihre Merkmale nur Daten verwenden, die vor dem Ereignis verfügbar sind. Andernfalls “schummelt” das Modell.
Schritt 5: Wählen Sie den richtigen KI-Ansatz (und wo LLMs passen)
Verschiedene DeFi-Fragen entsprechen verschiedenen Modellfamilien.
A. Zeitreihenprognose (wenn Dynamik wichtig ist)
Verwenden Sie, wenn Sie vorhersagen:
B. Klassifikation & Ranking (wenn Sie „Top-Kandidaten“ auswählen)
Verwenden Sie, wenn Sie benötigen:
C. Anomalieerkennung (wenn Sie den Angriff noch nicht kennen)
Nützlich für:
D. Graph-Lernen (wenn Beziehungen das Signal sind)
On-Chain ist natürlich ein Graph: Wallets ↔ Verträge ↔ Pools ↔ Vermögenswerte. Graph-basierte Merkmale können flache Tabellen übertreffen für:
Wo LLMs helfen (und wo nicht)
LLMs sind großartig für:
LLMs sind kein Ersatz für:
Ein praktisches Hybrid:
Schritt 6: Bewertung und Backtesting (der nicht verhandelbare Teil)
DeFi ist nicht stationär. Wenn Sie nicht sorgfältig bewerten, ist Ihr „Signal“ eine Illusion.
A. Nach Zeit aufteilen, nicht zufällig
Verwenden Sie zeitbasierte Aufteilungen:
B. Sowohl Genauigkeit als auch Entscheidungsqualität verfolgen
In DeFi kümmern Sie sich oft um Ranking und Risiko, nicht nur um „Genauigkeit“.
Eine einfache Bewertungscheckliste
1. Definieren Sie die Entscheidungsregel (z. B. „vermeiden, wenn das Risiko-Score > 0,7“)
2. Backtesten mit Transaktionskosten- & Slippage-Annahmen
3. Führen Sie Stressregime durch (hohe Gaspreise, hohe Volatilität, Liquiditätsengpass)
4. Vergleichen Sie mit Basislinien (einfache Heuristiken gewinnen oft)
5. Speichern Sie eine Audit-Trail (Merkmale, Modellversion, Snapshot-Blöcke)
| Bewertungsstufe | Was Sie messen | Warum es wichtig ist |
|---|---|---|
| Prädiktiv | AUC / Fehler | Signalqualität |
| Ökonomisch | PnL / Drawdown / Slippage | Realweltliche Lebensfähigkeit |
| Operativ | Latenz / Stabilität | Kann es täglich laufen? |
| Sicherheit | Falsche Positives/Negatives | Risikobereitschafts-Ausrichtung |
Schritt 7: Bereitstellen als Schleife (nicht als einmaliger Bericht)
Ein echtes „praktisches Workflow“ ist eine Schleife, die Sie jeden Tag/Woche ausführen können.
Kernproduktionsschleife
Überwachung, die in DeFi wichtig ist
Praktische Regel: Wenn Sie nicht erklären können, warum das Modell seinen Score geändert hat, können Sie ihm in einem reflexiven Markt nicht vertrauen.
Ein praktisches Beispiel: „Ist dieser APY echt?“
Lass uns den Workflow auf eine häufige DeFi-Falle anwenden: attraktive Renditen, die größtenteils Anreize sind.
Schritt-für-Schritt
Berechnen:
fee_revenue_usd (Handelsgebühren / Kreditkosten)incentives_usd (Emissionen + Bestechungen + Belohnungen)net_inflows_usd (ist TVL organisch oder mercenary?)user_return_estimate (Gebühreneinnahmen minus IL / Kreditkosten, wo relevant)Ein einfaches Nachhaltigkeitsverhältnis:
fee_to_incentive = fee_revenue_usd / max(incentives_usd, 1)Interpretation:
fee_to_incentive > 1.0 deutet oft auf gebührenunterstützte Renditen hinfee_to_incentive < 0.3 deutet darauf hin, dass Anreize dominieren| Kennzahl | Was es dir sagt | Warnschwellenwert |
|---|---|---|
| feetoincentive | gebührenunterstützt vs Emissionen | < 0.3 |
| TVL-Fluktuation | mercenary Liquidität | hohe wöchentliche Fluktuation |
| Walanteil | Konzentrationsrisiko | Top 5 > 40% |
| MEV-Intensität | Ausführungs-Toxizität | steigende Sandwich-Rate |
| Nettogebühren pro TVL | Effizienz | fallender Trend |
KI hinzufügen:
fee_revenue_usd unter mehreren Volumenszenarien
Wie funktioniert KI für DeFi-Datenanalyse on-chain?
AI für DeFi-Datenanalyse funktioniert on-chain, indem es niedrigstufige Blockchain-Artefakte (Transaktionen, Protokolle, Rückverfolgbarkeiten und Zustände) in ökonomische Merkmale (Gebühren, Hebel, Liquiditätstiefe, Risikokonzentration) umwandelt und dann Muster lernt, die Ergebnisse vorhersagen, die Sie messen können (Ertragsnachhaltigkeit, Liquiditätsschocks, Insolvenzrisiko, anomale Ströme). Der „AI“-Teil ist nur so gut wie:
Wenn Sie den Workflow als wiederholbares System betrachten – ähnlich dem gestuften Forschungsansatz, der in der SimianX-ähnlichen mehrstufigen Analyse betont wird – erhalten Sie Modelle, die sich im Laufe der Zeit verbessern, anstatt brüchige einmalige Erkenntnisse.
Praktische Werkzeuge: ein minimales Stack, das Sie tatsächlich betreiben können
Sie benötigen kein großes Team, aber Sie brauchen Disziplin.
A. Datenebene
B. Analytik-Ebene
C. „Forschungsagent“-Ebene (optional, aber leistungsstark)
Hier glänzt eine Multi-Agenten-Denkweise:
Hier kann auch SimianX AI ein hilfreiches mentales Modell sein: Anstatt sich auf eine einzige „allwissende“ Analyse zu verlassen, nutzen Sie spezialisierte Perspektiven und zwingen Sie zu expliziten Abwägungen – und erstellen Sie dann einen klaren, strukturierten Bericht. Sie können den Plattformansatz bei SimianX AI erkunden.
Häufige Fehlermodi (und wie man sie vermeidet)
FAQ zur KI für DeFi-Datenanalyse: Ein praktischer On-Chain-Workflow
Wie baut man On-Chain-Funktionen für maschinelles Lernen in DeFi auf?
Beginnen Sie mit den Protokollmechanismen: Ordnen Sie Ereignisse der Ökonomie zu (Gebühren, Schulden, Sicherheiten, Liquiditätstiefe). Verwenden Sie rollierende Fenster, vermeiden Sie Leckagen und speichern Sie Funktionsdefinitionen mit Versionierung, damit Sie Ergebnisse reproduzieren können.
Was ist realer Ertrag in DeFi und warum ist er wichtig?
Der reale Ertrag ist der Ertrag, der hauptsächlich durch organische Protokollumsätze (Gebühren/Zinsen) und nicht durch Tokenemissionen gedeckt ist. Er ist wichtig, weil Emissionen verblassen können, während gebührenbasierte Renditen oft bestehen bleiben (obwohl sie immer noch zyklisch sein können).
Was ist der beste Weg, um DeFi-Signale zu backtesten, ohne sich selbst zu täuschen?
Teilen Sie nach Zeit, berücksichtigen Sie Transaktionskosten und Slippage und testen Sie über Stressregime hinweg. Vergleichen Sie immer mit einfachen Baselines; wenn Ihr Modell eine Heuristik nicht zuverlässig übertreffen kann, ist es wahrscheinlich überangepasst.
Können LLMs quantitative On-Chain-Analysen ersetzen?
LLMs können die Interpretation beschleunigen – Vorschläge zusammenfassen, Annahmen extrahieren, Checklisten organisieren – aber sie können die korrekte Ereignisdekodierung, rigoroses Labeling und zeitbasierte Bewertungen nicht ersetzen. Verwenden Sie LLMs, um die Forschung zu strukturieren, nicht um die Kette zu „halluzinieren“.
Wie erkenne ich anreizgetriebene (mercenary) Liquidität?
Verfolgen Sie den TVL-Abgang, die Verhältnisse von Gebühren zu Anreizen und die Zusammensetzung der Wallet-Kohorten. Wenn Liquidität erscheint, wenn die Anreize steigen, und schnell danach wieder verschwindet, behandeln Sie die Rendite als fragil, es sei denn, die Gebühren unterstützen sie unabhängig.
Fazit
KI wird im DeFi-Bereich wirklich wertvoll, wenn Sie On-Chain-Geräusche in einen wiederholbaren Arbeitsablauf umwandeln: entscheidungsorientierte Rahmenbedingungen, reproduzierbare Datensätze, konservative Entitätskennzeichnung, mechanismenbasierte Merkmale, zeitlich aufgeteilte Bewertungen und kontinuierliche Überwachung. Folgen Sie diesem praktischen On-Chain-Zyklus, und Sie werden Analysen produzieren, die über Protokolle hinweg vergleichbar, widerstandsfähig gegenüber Regimewechseln und für Teamkollegen oder Stakeholder erklärbar sind.
Wenn Sie eine strukturierte Möglichkeit suchen, gestufte, multiperspektivische Forschung durchzuführen (und komplexe Daten in klare, teilbare Ergebnisse zu übersetzen), erkunden Sie SimianX AI als Modell zur Organisation rigoroser Analysen in einen umsetzbaren Arbeitsablauf.



