IA para Modelar a Volatilidade e Reações em Cadeia dos Riscos DeFi
DeFi geralmente não falha por causa de uma única “negociação ruim.” Ela falha porque choques de volatilidade se propagam através de liquidez, alavancagem e camadas de incentivo—e uma pequena fissura se torna uma reação em cadeia. É exatamente por isso que IA para modelar a volatilidade e reações em cadeia dos riscos DeFi está se tornando uma necessidade prática para qualquer um que aloque capital sério em cadeia. Neste guia de pesquisa, construiremos uma estrutura rigorosa: como é a “contágio” em DeFi, quais características em cadeia importam e como métodos modernos de IA podem simular cascatas antes que elas aconteçam. Também mostraremos como as equipes podem operacionalizar esses modelos dentro de um fluxo de trabalho de pesquisa repetível com ferramentas como SimianX AI.

1) O que “reações em cadeia” significam em DeFi (e por que a volatilidade é o gatilho)
Nas finanças tradicionais, o contágio frequentemente flui através de balanços e mercados de financiamento. Em DeFi, o contágio é codificado em protocolos e amplificado pela composabilidade:
Um “choque” DeFi tipicamente começa com um impulso de volatilidade:
Insight chave: Em DeFi, a volatilidade não é apenas uma condição de mercado—ela é frequentemente o mecanismo que transforma risco local em risco sistêmico.
Um modelo mental simples: Risco DeFi como uma pilha em camadas
Pense na sua posição como se estivesse sentado em uma pilha:
1. Camada de mercado: volatilidade do ativo subjacente, correlação, condições de financiamento
2. Camada de liquidez: capacidade de saída, deslizamento, profundidade, comportamento de LP
3. Camada de mecanismo: regras de liquidação, oráculos, modelos de taxa, disjuntores
4. Camada de incentivo: emissões, subornos, governança, capital mercenário
5. Camada operacional: atualizações, chaves administrativas, dependências, interrupções
“Reações em cadeia” acontecem quando o estresse se move para baixo ou para cima na pilha rapidamente.
2) Um modelo de dados: o que você deve medir para modelar cascatas
Se você não pode medir, você não pode simular. Para cascatas DeFi, você precisa de características que capturem (a) regime de volatilidade, (b) concentração de alavancagem, e (c) atrito de saída.
Famílias de características principais (práticas e mensuráveis)
| Família de características | O que mede | Sinais de exemplo (on-chain) | Por que é importante para cascatas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volatilidade & regime | Se o sistema está calmo ou estressado | vol realizada, autocorrelação de retorno, frequência de saltos, oscilações de financiamento | mudanças de regime alteram a probabilidade de liquidação de forma não linear |
| Liquidez & deslizamento | Quão custoso é sair | sensibilidade da curva AMM, profundidade do pool, base CEX/DEX, fragmentação de roteamento | liquidez rasa transforma liquidações em impacto de preço |
| Alavancagem & concentração | Quem é liquidado primeiro, e quão severamente | utilização de empréstimo, concentração de colateral, posições de baleias, distribuição do fator de saúde | alavancagem agrupada causa “liquidações em dominó” |
| Fragilidade do oráculo | Integridade do preço sob estresse | frequência de atualização do oráculo, medianização, bandas de desvio, divergência DEX-CEX | oráculos podem transmitir ou amplificar choques |
| Saúde do peg da stablecoin | Se a unidade de conta quebra | desvio de peg, filas de resgate, desvio da qualidade da garantia | desvinculações reescrevem todos os cálculos de risco instantaneamente |
| Reflexividade de incentivo | TVL que pode desaparecer da noite para o dia | participação de emissão APR, churn de LP mercenário, dependência de suborno | incentivos frequentemente desaparecem exatamente quando mais são necessários |
Regras de higiene de dados (não negociáveis):
É aqui que plataformas como SimianX AI podem ajudar: você quer um pipeline documentado e repetível que transforme a atividade barulhenta na cadeia em características defensáveis e suposições versionadas.
3) Modelando a volatilidade: de regimes a “probabilidade de choque”
A modelagem de volatilidade não é apenas prever retornos. Para o risco DeFi, você está prevendo a probabilidade de estresse estrutural.
Uma escada prática de modelagem de volatilidade
Nível 1 — Linhas de base (rápido, robusto):
EWMA)VaR, CVaR)Nível 2 — Detecção de regime (o que você realmente precisa):
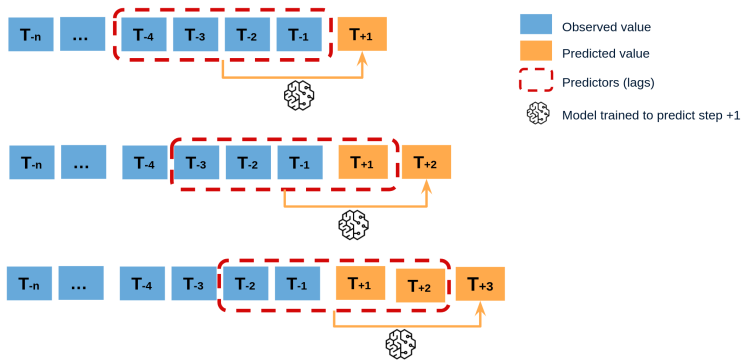
Nível 3 — Modelos de sequência ML/AI (quando você tem dados suficientes):
Regra prática: Para DeFi, o melhor objetivo muitas vezes não é “prever o preço.” É “prever estado de estresse e sua probabilidade de transição.”
O que prever (alvos que mapeiam para risco real)
Em vez de prever next_return, defina alvos como:
P(liquidation_wave_next_24h)expected_slippage_at_size sob liquidez estressadaprobability_of_oracle_deviation_eventprobability_of_peg_break > x bpsEsses alvos estão mais próximos do que realmente elimina capital.
4) Modelando reações em cadeia: gráficos de contágio e dinâmicas de liquidação
Para modelar “reações em cadeia,” você precisa de estrutura: quem depende de quem, e quais vínculos se estreitam sob estresse.
4.1 Construa o gráfico de dependência DeFi
Represente o ecossistema como um gráfico direcionado:
Os pesos das arestas devem ser dependentes do estado:
Token A e Stablecoin S pode ser fracoA é um colateral importante para S, esse peso aumentaCaracterísticas do gráfico a serem rastreadas:
4.2 Modelagem de cascata de liquidação (o motor do contágio)
Liquidações são frequentemente o motor mecânico das reações em cadeia. Uma abstração útil:
1. Um conjunto de mutuários tem colateral C e dívida D
2. Uma queda de preço move fatores de saúde abaixo do limite
3. Liquidadores vendem colateral na liquidez disponível
4. O impacto no preço cria liquidações de segunda ordem
Você pode modelar essa cascata com:
Simulação baseada em agentes (ABM): a maneira mais intuitiva de testar cascatas
Use agentes representando:
ABM é poderoso porque o estresse em DeFi é comportamental e mecânico:
5) Métodos de IA que realmente ajudam (e onde falham)
A IA é útil quando o sistema é não linear, multivariado e dependente de regime—que é exatamente o DeFi.
No que a IA é ótima
No que a IA é ruim (se você não tomar cuidado)
Recomendação prática: Use IA como um radar de risco (detecção + geração de cenários) e combine-a com simulações mecanicistas (modelos de liquidação/impacto) para testes de estresse de grau de decisão.
Uma arquitetura híbrida robusta (recomendada)
stress_probability e prevê distribuições condicionais de variáveis de estado chaveEste é também onde SimianX AI se encaixa naturalmente como um fluxo de trabalho operacional: organizar a pesquisa em estágios consistentes, manter evidências anexadas às saídas e garantir que cada conclusão de risco seja reproduzível.
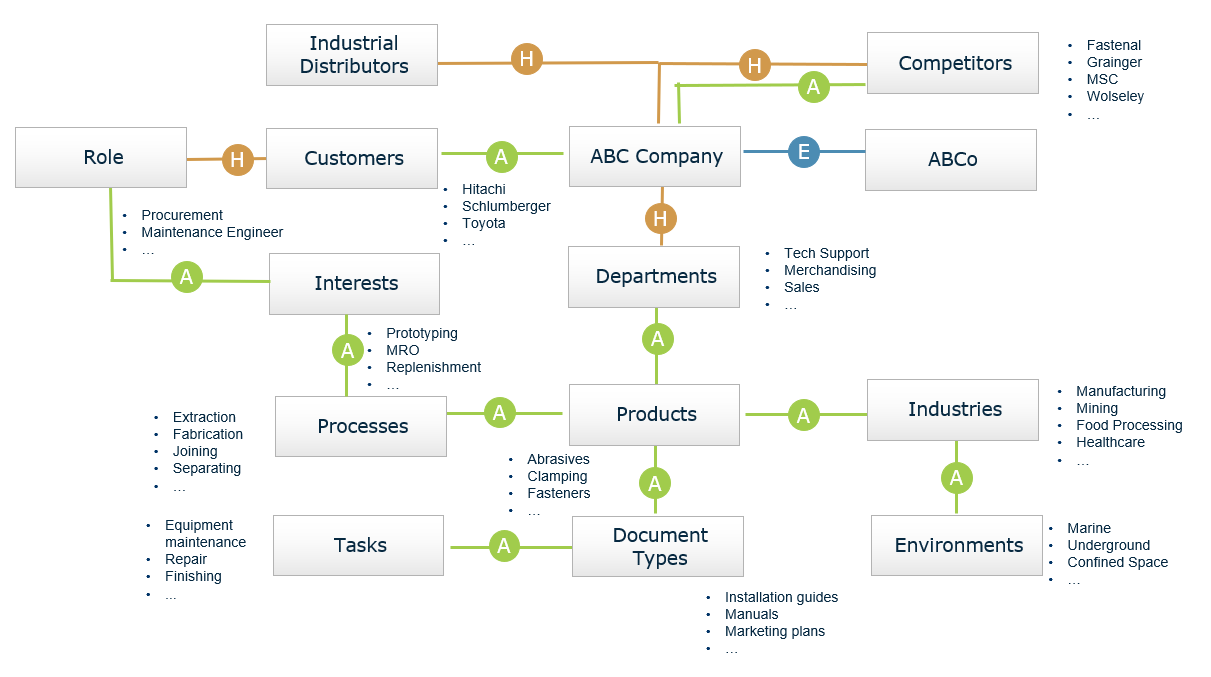
6) Passo a passo: um pipeline prático para modelar reações em cadeia de risco DeFi
Aqui está um pipeline concreto que você pode implementar para qualquer categoria de protocolo (empréstimos, stablecoins, estratégias de LP):
Passo 1 — Defina seus pontos finais de cascata
Escolha resultados que você se importa:
Passo 2 — Crie rótulos de “estado de estresse”
Crie rótulos a partir de eventos observáveis:
Passo 3 — Treine um classificador de estresse (interpretável primeiro)
Comece com algo que você pode explicar:
Depois itere para modelos de sequência se necessário.
Passo 4 — Gere cenários condicionais
Em vez de uma previsão, gere uma distribuição:
Passo 5 — Execute simulações de cascata
Para cada cenário:
1. simule fatores de saúde do tomador
2. simule volumes de liquidação
3. simule impacto no mercado e caminhos de preços
4. reavalie fatores de saúde → itere até estabilizar
Passo 6 — Converta resultados em ações de risco
Exemplos:
P(cascade) > thresholdLista numerada (operacional):
1. Congelar uma versão do conjunto de dados e conjunto de recursos
2. Testar retroativamente em janelas de estresse passadas
3. Calibrar limites para evitar "alarme constante"
4. Adicionar monitoramento para desvio de recursos
5. Documentar suposições e modos de falha
7) Como a IA pode modelar a volatilidade e as reações em cadeia dos riscos DeFi em tempo real?
A modelagem em tempo real é menos sobre “inferência mais rápida” e mais sobre atualizações de estado mais rápidas.
O loop em tempo real (o que importa)
Sinais em tempo real que valem a pena priorizar
Se você apenas monitorar preços, você está atrasado. O risco DeFi em tempo real é sobre monitorar as restrições que transformam movimentos de preço em insolvência.
8) Avaliação: como saber se seu modelo é útil (não apenas sofisticado)
Um modelo de risco DeFi deve ser julgado por utilidade de decisão, não apenas por pontuações de previsão.
Métricas de avaliação úteis
Uma tabela de avaliação simples
| Pergunta de avaliação | Como é "bom" | Como é "ruim" |
|---|---|---|
| Ele avisa cedo? | tempo de antecedência consistente antes do estresse | só dispara após o dano |
| Está calibrado? | 70% significa ~70% na prática | probabilidades excessivamente confiantes |
| Ele generaliza? | funciona em diferentes ativos/cadeias | se encaixa apenas em um regime |
| Ele melhora decisões? | menores quedas / melhores saídas | nenhum benefício mensurável |
FAQ Sobre IA para Modelar a Volatilidade e Reações em Cadeia dos Riscos de DeFi
Qual é a melhor maneira de modelar cascatas de liquidação de DeFi?
Comece com um simulador de cascata mecanicista (fatores de saúde + impacto no mercado), depois condicione cenários com um modelo de estresse de IA. A combinação captura tanto a física quanto os sinais da contágio de DeFi.
Como modelar cascatas de risco de DeFi sem atribuição perfeita de carteira?
Use características distributivas (histogramas de fatores de saúde, índices de concentração, exposição dos principais mutuários) em vez de identidade por entidade. Você ainda pode simular cascatas com variáveis de estado agregadas e suposições conservadoras.
O que causa mais frequentemente cascatas de liquidação de DeFi?
Um choque de volatilidade mais um abismo de liquidez é a combinação clássica: preços em queda acionam liquidações, e a liquidez fina faz com que essas liquidações empurrem os preços ainda mais para baixo. Instabilidade de oráculo ou de paridade pode amplificar o ciclo.
A IA pode prever despegos de stablecoins de forma confiável?
A IA pode fornecer probabilidades de alerta precoce usando padrões de desvio de paridade, deriva na qualidade da garantia, condições de liquidez e proxies de pressão de resgate. Mas despegos são mudanças de regime—trate a IA como um radar probabilístico, depois teste mecanicamente as consequências.
Como monitorar o risco de cauda DeFi em tempo real?
Priorize variáveis de estado que representam restrições: profundidade de liquidez, utilização, desvio de peg, divergência de oráculo e grandes retiradas de LP. O risco de cauda é frequentemente visível na infraestrutura do sistema antes de aparecer no preço.
Conclusão
Usar IA para modelar a volatilidade DeFi é valioso—mas a verdadeira vantagem vem de modelar como a volatilidade se torna contágio: mecânicas de liquidação, penhascos de liquidez, dependências de oráculo e fragilidade de peg. Um fluxo de trabalho forte combina (1) probabilidades de estresse de IA ciente do regime, (2) geração de cenários e (3) simulação de cascata mecanicista que traduz estresse em custos de saída e risco de insolvência. Se você deseja operacionalizar isso em um ciclo de pesquisa repetível—recursos, simulações, painéis e suposições documentadas—explore SimianX AI e construa seus modelos de risco DeFi como sistemas, não opi:contentReference[oaicite:0]{index=0}
::contentReference[oaicite:1]{index=1}



