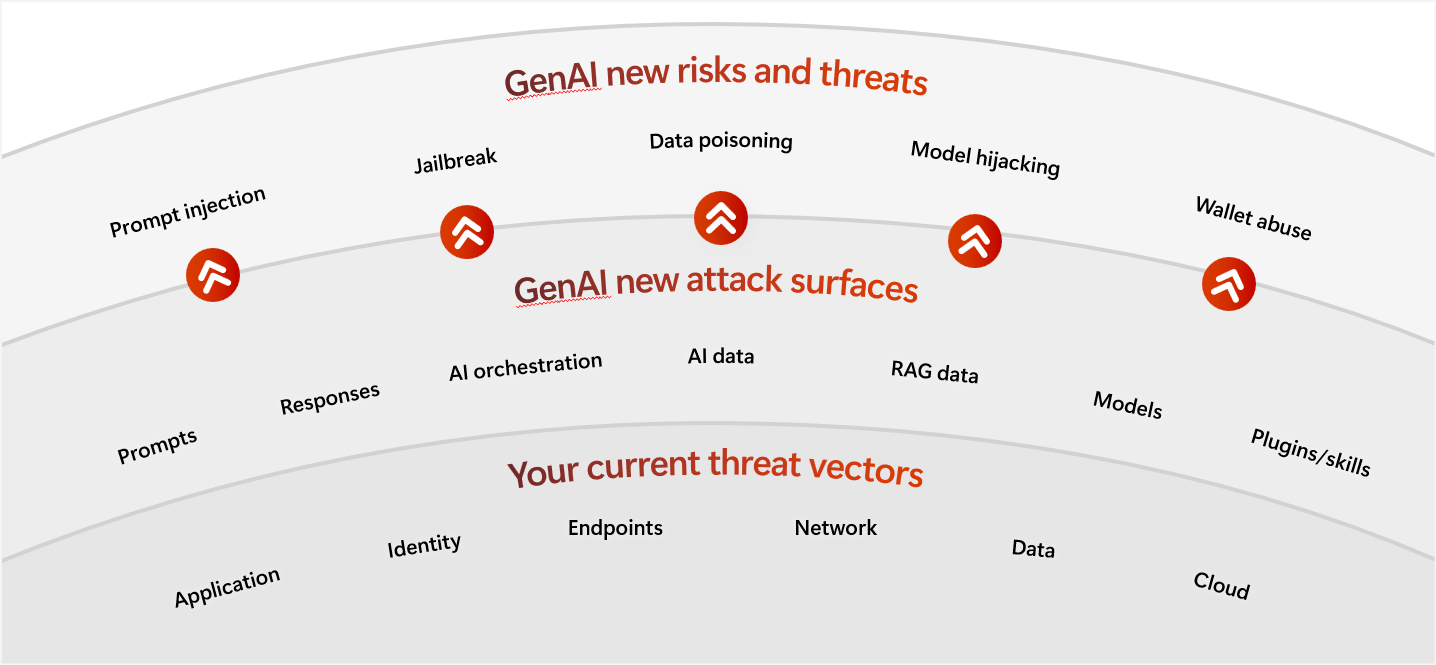
Специализированные модели временных рядов против LLM для прогнозирования цен на криптовалюту
Специализированные модели временных рядов против LLM для прогнозирования цен на криптовалюту стали одной из самых обсуждаемых тем в исследованиях торговли с использованием ИИ. Поскольку крипторынки становятся все более сложными, трейдеры и исследователи сталкиваются с критическим выбором: полагаться на математически обоснованные модели временных рядов или использовать большие языковые модели (LLM), изначально созданные для текста, но все чаще применяемые для рыночной аналитики.
В этой статье мы исследуем, как эти две группы моделей различаются, где каждая из них преуспевает и как платформы, такие как SimianX AI, помогают объединить их в более надежные системы прогнозирования криптовалют.
Почему прогнозирование цен на криптовалюту является уникальной задачей моделирования
Крипторынки принципиально отличаются от традиционных финансовых рынков:
Эти свойства ставят под сомнение любую единую парадигму моделирования.
В криптовалюте структура и история имеют одинаковое значение — и немногие модели захватывают оба аспекта.
Понимание этой двойственности является ключевым при сравнении специализированных моделей временных рядов и LLM.
Что такое специализированные модели временных рядов?
Специализированные модели временных рядов созданы специально для анализа последовательных числовых данных. Они предполагают, что цены следуют определенным статистическим свойствам во времени.
Общие категории включают:
Ключевые сильные стороны:
Основные слабости:

Как работают модели временных рядов на крипторынках
Модели временных рядов обычно полагаются на:
1. Историю цен и объемов
2. Запаздывающие корреляции
3. Предположения о стационарности
4. Инженерия признаков
| Аспект | Модели временных рядов |
|---|---|
| Тип данных | Только числовые |
| Интерпретируемость | Высокая |
| Реакция на новости | Косвенная |
| Осведомленность о режиме | Ограниченная |
Эти модели превосходны в стабильных микро-режимах, но часто терпят неудачу, когда доминируют нарративы или шоки ликвидности.
Что такое LLM в прогнозировании цен на криптовалюту?
LLM не были разработаны для прогнозирования цен. Тем не менее, их способность моделировать язык, контекст и рассуждение открыла новые случаи использования на крипторынках.
LLM все чаще используются для:
Сильные стороны:
Слабости:

Почему LLM испытывают трудности с прогнозированием цен в сыром виде
LLM не имеют встроенного индуктивного смещения для временной непрерывности. Цены токенизированы, а не моделируются во времени.
В результате:
LLM лучше интерпретаторы рынка, чем калькуляторы цен.

Специализированные модели временных рядов против LLM: Прямое Сравнение
| Размерность | Модели временных рядов | LLMs |
|---|---|---|
| Числовая точность | Высокая | Низкая–Средняя |
| Осведомленность о контексте | Низкая | Очень высокая |
| Реакция на новости | Медленная | Быстрая |
| Обнаружение режимов | Слабое | Сильное |
| Объяснимость | Математическая | Лингвистическая |
| Эффективность данных | Высокая | Низкая |
Это сравнение подчеркивает, почему ни один из подходов не является достаточным.

Когда модели временных рядов превосходят LLM
Модели временных рядов доминируют, когда:
Примеры включают:
Эти условия способствуют точности над интерпретацией.
Когда LLM превосходят модели временных рядов
LLM блестят во время:
Они определяют почему рынки движутся, а не только как.
Примеры:

Почему гибридные архитектуры — это будущее
Самые эффективные системы прогнозирования криптовалют интегрируют оба подхода.
Общая архитектура:
1. Модели временных рядов генерируют числовые прогнозы
2. LLM интерпретируют контекст, нарративы и аномалии
3. Мета-модели согласовывают конфликты и управляют неопределенностью
| Уровень | Роль |
|---|---|
| Числовой уровень | Краткосрочные ценовые сигналы |
| Семантический уровень | Интерпретация нарратива и риска |
| Уровень принятия решений | Логика портфеля или исполнения |
Это философия многопользовательской исследовательской структуры SimianX AI.

Как SimianX AI использует модели временных рядов и LLM вместе
SimianX AI рассматривает прогнозирование криптовалют как проблему систем, а не как задачу единственной модели.
На платформе:
Это снижает переобучение, галлюцинации и ложную уверенность.
Вы можете исследовать этот подход напрямую на
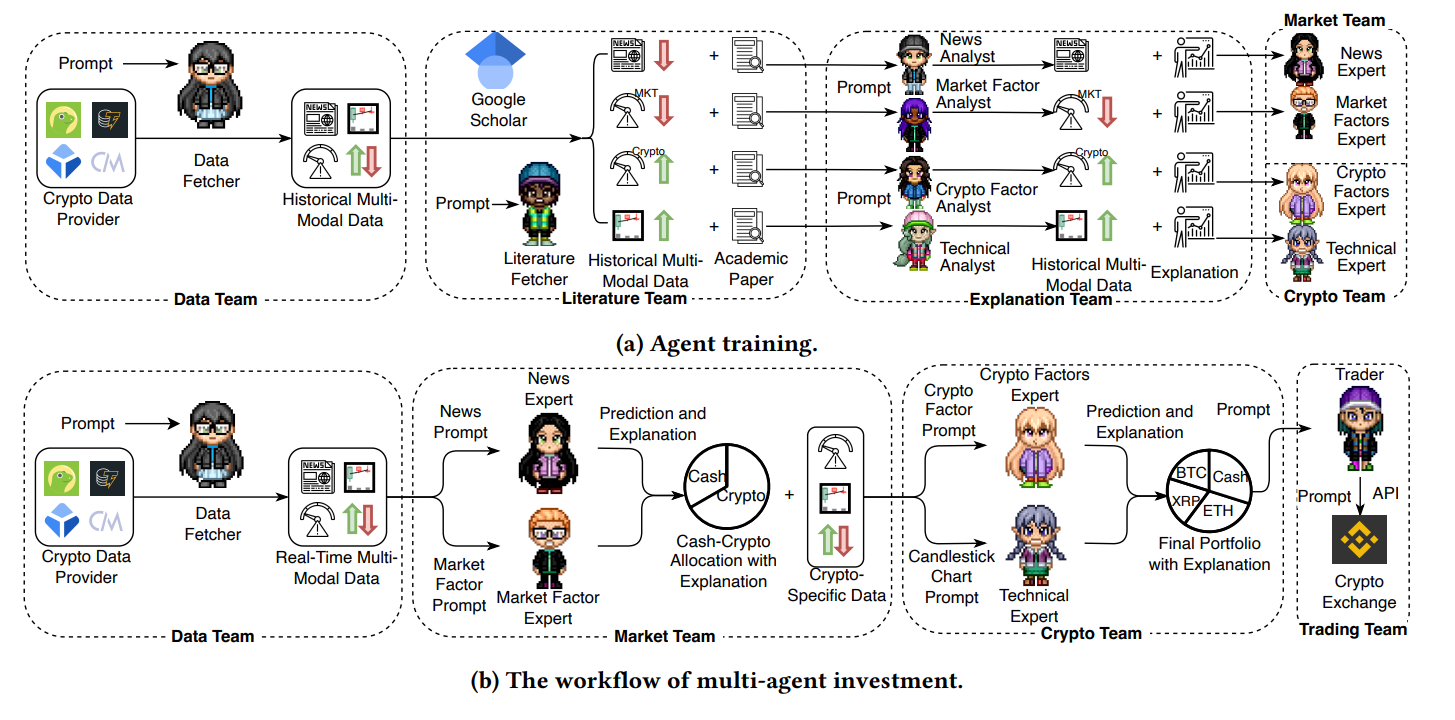
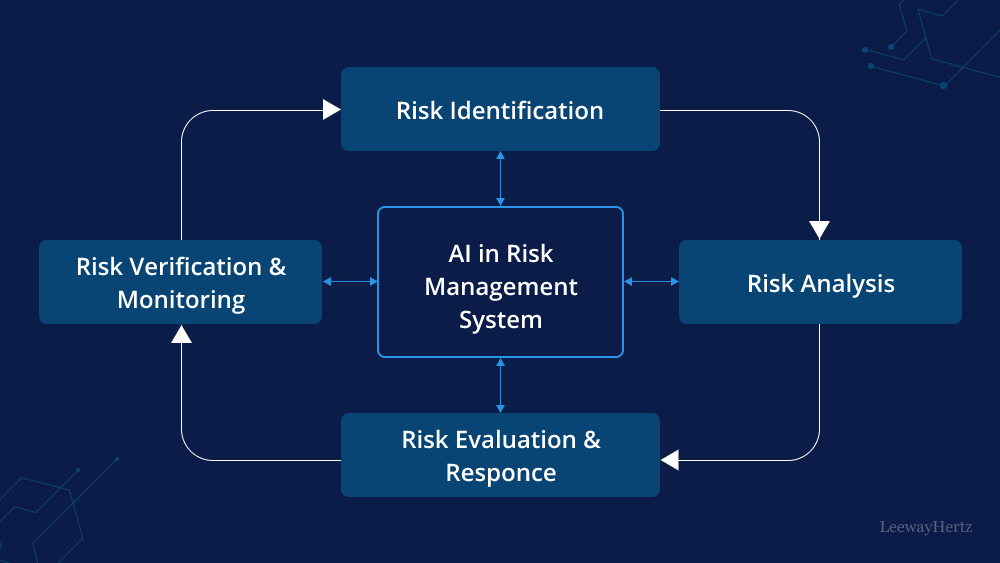
Почему многоагентные системы важны для прогнозирования
Единственные модели терпят молчаливый провал. Многоагентные системы терпят громкий провал.
Преимущества включают:
В криптовалюте умение не торговать так же ценно, как точность прогнозирования.
Практическое руководство: Какую модель вам следует использовать?
Используйте модели временных рядов, если вам нужны:
Используйте LLM, если вам нужно:
Используйте оба, если хотите выживаемость в разных рыночных режимах.

Часто задаваемые вопросы о специализированных моделях временных рядов против LLM для прогнозирования цен на криптовалюту
Хороши ли LLM для прогнозирования цен на криптовалюту?
LLM слабы в прямом числовом прогнозировании, но сильны в интерпретации нарративов, настроений и изменений режимов, которые движут крипторынками.
Имеют ли значение модели временных рядов в криптовалюте?
Да. Модели временных рядов остаются необходимыми для краткосрочной точности, моделирования волатильности и стратегий на уровне исполнения.
Какой лучший ИИ-модель для прогнозирования криптовалют?
Нет единственной лучшей модели. Гибридные системы, объединяющие модели временных рядов и LLM, последовательно превосходят отдельные подходы.
Могу ли я использовать LLM для торговых сигналов?
LLM не должны генерировать сырые торговые сигналы самостоятельно. Их лучше использовать как контекстуальные или осведомленные о рисках слои, поддерживающие числовые модели.
Заключение
Специализированные модели временных рядов против LLM для прогнозирования цен на криптовалюту — это не вопрос замены, а интеграции. Модели временных рядов обеспечивают числовую дисциплину, в то время как LLM предоставляют нарративный интеллект и адаптивное мышление.
Будущее прогнозирования криптовалют принадлежит гибридным, многоагентным системам, которые понимают как цены, так и людей.
Если вы хотите исследовать этот подход следующего поколения, посетите
SimianX AI и узнайте, как скоординированные ИИ-агенты могут помочь вам ориентироваться на крипторынках с ясностью и контролем.
---
Глубокое погружение: Почему чистое прогнозирование цен терпит неудачу на крипторынках
Одно из самых неправильно понятых предположений в криптоисследованиях заключается в том, что прогнозирование цен является конечной целью. На самом деле, прогнозирование цен является лишь заменой для принятия решений в условиях неопределенности.
Крипторынки нарушают почти все классические предположения:
В результате, метрики точности сами по себе вводят в заблуждение.
Модель может быть направленно «правильной» и все равно вызвать катастрофические убытки.
Вот почему оценка специализированных моделей временных рядов против LLM для прогнозирования цен на криптовалюту требует переосмысления проблемы:
прогнозирование не касается цен — это касается действий с учетом риска.
---
Скрытые режимы отказа моделей временных рядов в крипто
Специализированные модели временных рядов терпят неудачу не потому, что они слабы, а потому, что крипторынки часто работают вне их проектного диапазона.
1. Коллапс режима
Модели временных рядов предполагают непрерывность. Крипторынки разрывают непрерывность.
Примеры:
Эти события вводят структурные разрывы, мгновенно аннулируя изученные параметры.
2. Смещение признаков и переобучение
Криптоиндикаторы быстро теряют актуальность.
| Тип признака | Период полураспада |
|---|---|
| Импульс | Часы–Дни |
| Всплески объема | Минуты–Часы |
| Волатильность | Зависит от режима |
| Метрики на блокчейне | Обусловлены нарративом |
Без постоянного переобучения модели временных рядов тихо деградируют.
3. Ложная уверенность в условиях стресса
Модели временных рядов выдают числа, а не сомнения.
Это создает иллюзию уверенности именно тогда, когда неопределенность наивысшая.
В криптовалюте молчание модели часто более опасно, чем шум.
---
Скрытые режимы отказа LLM в криптовалюте
Хотя LLM прекрасно справляются с семантическим рассуждением, они вводят новые классы рисков.
1. Переобучение нарратива
LLM переоценивают доминирующие нарративы.
Примеры:
Это приводит к поведенческому стадному эффекту на уровне модели.
2. Темпоральная галлюцинация
LLM не испытывают время — они делают выводы о нем.
Последствия:
3. Уверенность без калибровки
LLM выражают неопределенность лингвистически, а не вероятностно.
Это затрудняет:
---
Почему точность прогнозирования — это неправильная цель оптимизации
Большинство крипто AI систем оптимизируют для:
Эти метрики игнорируют капитальную динамику.

Лучшие цели оптимизации
Более реалистичная целевая функция включает:
| Метрика | Почему это важно |
|---|---|
| Максимальная просадка | Выживание |
| Условный VaR | Риск хвоста |
| Оборот | Исполнительное трение |
| Уровень ошибки режима | Структурный риск |
Здесь гибридные системы превосходят подходы с одним моделем.
---
Гибридный интеллект: от моделей к когнитивным системам
Будущее прогнозирования криптовалют не в лучших моделях, а в лучших системах.
Гибридные архитектуры рассматривают модели как агентов, а не как оракулов.

Роли агентов в гибридной системе
1. Агенты временных рядов
2. Агенты LLM
3. Мета-агенты
Прогнозирование становится разговором, а не расчетом.
---
Как SimianX AI реализует многопользовательское прогнозирование
SimianX AI операционализирует эту философию через координированную исследовательскую архитектуру.
Ключевые принципы дизайна:
Пример: Обнаружение рыночного шока
Когда происходит шок:
1. Агенты временных рядов обнаруживают аномальную волатильность
2. Агенты LLM анализируют нарративные триггеры
3. Мета-агент оценивает величину разногласий
4. Система снижает уверенность и экспозицию
Это предотвращает избыточную приверженность модели.
---
Кейс: Ралли, основанное на нарративе, против структурной слабости
Рассмотрим гипотетический рыночный сценарий:
Взгляд модели временных рядов
Взгляд LLM
Разрешение мета-агента
Это то, как прогнозирование становится осознанным рисковым интеллектом.
---
Переосмысление горизонтов прогнозирования в криптовалюте
У криптовалюты нет единого "будущего".
Разные горизонты ведут себя как разные рынки.
| Горизонт | Доминирующий фактор |
|---|---|
| Минуты | Поток заказов |
| Часы | Кластеризация волатильности |
| Дни | Наративный импульс |
| Недели | Ликвидность и макроэкономика |
| Месяцы | Структурное принятие |
Модели временных рядов доминируют на коротких горизонтах.
LLM доминируют на средних горизонтах.
Только гибридные системы охватывают все горизонты последовательно.
---
От прогнозирования к политике: ИИ как управляющий рынком
Самые продвинутые криптовалютные системы не прогнозируют — они управляют риском.

Политики ИИ включают:
Это меняет роль ИИ с трейдера на управляющего риском.
---
Почему большинство розничных инструментов ИИ для криптовалют терпят неудачу
Розничные "торговые боты ИИ" часто терпят неудачу, потому что они:
Модель, которая никогда не говорит "Я не знаю", опасна.
---
Институциональные уроки из исследований прогнозирования криптовалют
Учреждения, входящие в криптовалюту, должны разучить предположения TradFi:
Это делает интеграцию LLM + временных рядов обязательной, а не опциональной.
---
Проектирование собственного гибридного стека прогнозирования криптовалют
Минимальная архитектура:
1. Слой числовых сигналов
2. Слой интерпретации нарратива
3. Слой арбитража рисков
4. Слой управления исполнением

Это концептуальный чертеж SimianX AI.
---
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ: Продвинутые вопросы о гибридном прогнозировании криптовалют
Почему не просто обучить более крупные модели временных рядов?
Масштаб не решает неопределенность режимов. Более крупные модели быстрее переобучаются на нестабильных рынках.
Могут ли LLM заменить количественные модели?
Нет. LLM не имеют числовой основы и никогда не должны работать без количественных ограничений.
Как многопользовательские системы уменьшают убытки?
Путем выявления разногласий на ранней стадии и ограничения воздействия, когда уверенность падает.
Полезен ли прогноз, если точность низка?
Да—если прогноз информирует контроль рисков, а не слепое выполнение.
---
Заключение: Конец мышления, ориентированного на модели
Дебаты о специализированных моделях временных рядов против LLM для прогнозирования цен на криптовалюту в конечном итоге неуместны.
Настоящая эволюция заключается в:
модели → агенты → системы → управление
Модели временных рядов обеспечивают дисциплину.
LLM обеспечивают смысл.
Гибридные системы обеспечивают выживаемость.
Если вы строите или оцениваете инфраструктуру прогнозирования криптовалют, вопрос больше не в том, какая модель лучше, а в том:
Какая система терпит неудачу наиболее грациозно, когда рынки рушатся?
Изучите, как работает многопользовательский криптоинтеллект на практике на
---



